Basics Of Cloud Computing
The Only Article you Will Ever Need to Understand Cloud Computing
IN THIS BLOG YOU WILL DISCOVER
What cloud services are
What Cloud Computing is
Types of cloud computing
Cloud computing service providers
Pros and Cons of cloud services
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Types of cloud services
Uses of cloud computing
Introduction
In order to provide quicker innovation, adaptable resources, and scale economies, cloud computing, in its simplest form, is the supply of computing services via the Internet ("the cloud"), encompassing servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence.
Typically, you only pay for the cloud services you actually use, which lowers operational expenses, improves infrastructure management, and enables you to scale as your company's needs evolve.
What are cloud services?
A variety of services are referred to as "cloud services" and are made available to businesses and consumers online on demand. These services are created to offer quick, inexpensive access to resources and applications without the need for internal hardware or infrastructure.
Most employees utilize cloud services throughout the workday, whether they are aware of it or not, from checking email to working together on papers.
Cloud computing vendors and service providers are totally in charge of managing cloud services. There is no need for a business to host apps on its own in-house servers because they are made available to clients from the providers' servers.
What is cloud computing
Cloud computing is an overlay of computation, storage, and network infrastructure put together as a platform that allows for speedy application deployment and dynamic scaling. Self-service is crucial to cloud computing since it allows users to quickly and easily get started by filling out a web form.
Before the advent of cloud computing, companies had to buy and operate their own servers to suit business requirements. In order to accommodate peak traffic volume and lower the likelihood of outages and downtime, it was necessary to purchase enough server capacity. As a result, a sizable portion of the server's space was frequently unused. Companies can cut back on the requirement for expensive IT resources like onsite servers, maintenance staff, and other resources by using cloud service providers today.
The great majority of cloud users use public cloud computing services, which are hosted in sizable, distant data centers that are kept up by cloud providers, over the internet. SaaS (software as a service), the most popular kind of cloud computing, distributes prebuilt applications to the browsers of clients who pay per seat or by consumption, as demonstrated by well-known apps like Salesforce, Google Docs, or Microsoft Teams. The next option on the list is IaaS (infrastructure as a service), which provides extensive, virtualized compute, storage, and network infrastructure upon which users may build their own applications, frequently with the help of providers' API-accessible services.
Most frequently, when people casually refer to "the cloud," they are referring to the major IaaS providers, such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS (Amazon Web Services). The developer tools, serverless computing, machine learning services, and APIs, data warehouses, and thousands of more services that go far beyond infrastructure have all grown into enormous ecosystems. Agility is a major advantage of SaaS and IaaS. Customers can quickly scale the cloud resources they use up or down according to their needs while gaining new capabilities nearly immediately without making financial investments in hardware or software.
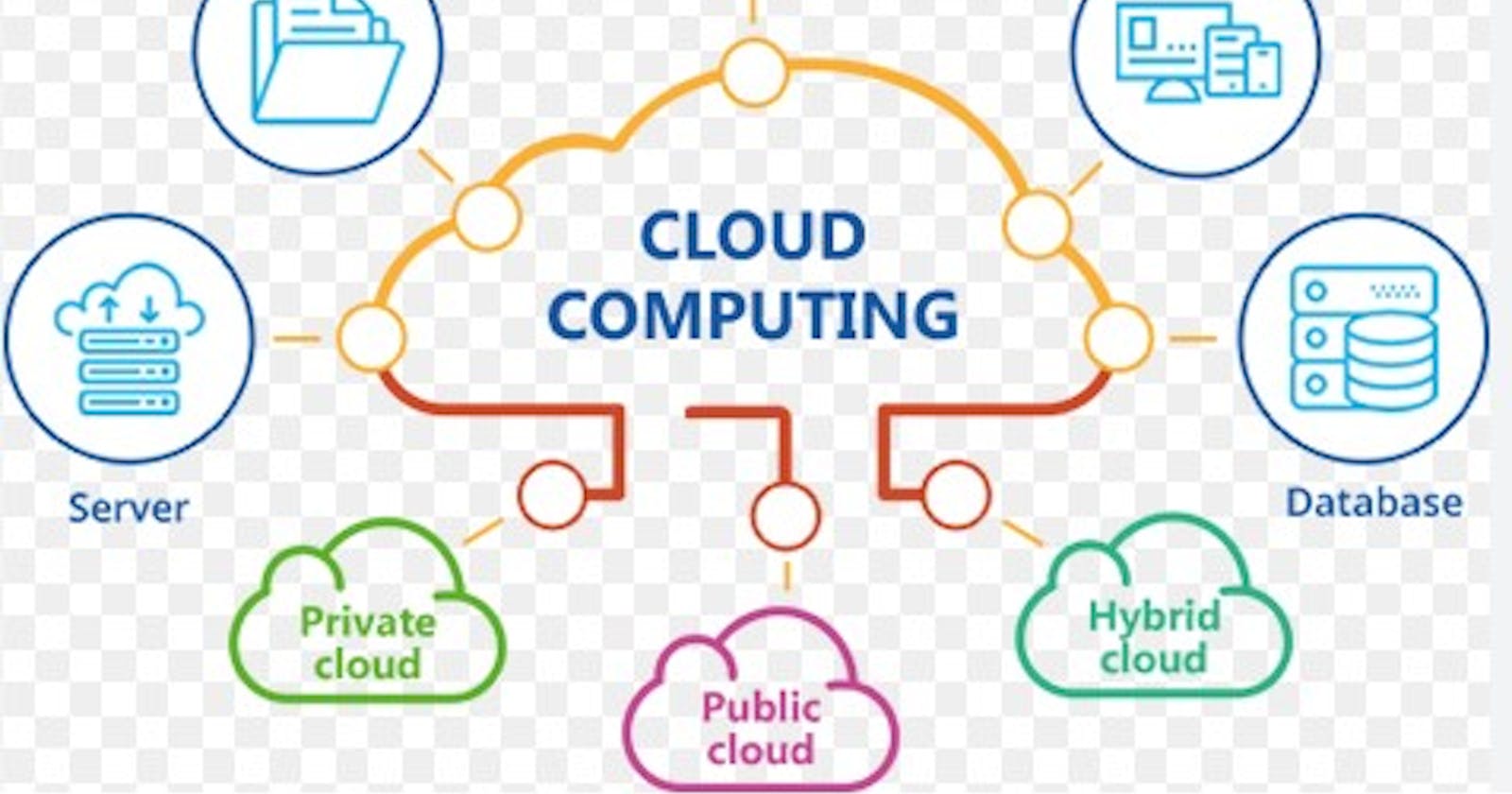
Types of cloud computing
on-premise cloud
private cloud
public cloud
hybrid cloud
multi-cloud
on-premise cloud
A word associated with cloud computing, on-premises cloud infrastructure, appears to go against a core tenant of cloud services, namely, that cloud services are often delivered off-site as a key component of cloud technology architecture. Hardware that is connected to cloud services or activities but is still present on-site at the client's actual business location is referred to as on-premises cloud infrastructure.
private cloud
Computing services delivered to a small group of customers only via a private internal network or the Internet as opposed to the broader public are referred to as private cloud services. e.g HPE GreenLake and Azure Stack.
public cloud
A third-party supplier manages on-demand computing services and infrastructure in the public cloud, which is a shared IT paradigm used by numerous enterprises on the open Internet. It is not necessary for users to host these services on-site in their own data center; instead, public cloud service providers may offer cloud-based services such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), or software as a service (Saas) to users for a monthly or pay-per-use fee. e.g Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, Google Cloud Platform, Oracle Cloud.
hybrid cloud
By combining private and public cloud models, hybrid cloud enables businesses to take advantage of shared resources while still leveraging their current IT infrastructure for vital security needs. Companies can store private information locally and access it using applications that are hosted in the public cloud thanks to the hybrid cloud approach. An enterprise may, for instance, keep sensitive customer data in a private cloud and carry out computations that require a lot of resources in the public cloud to abide by privacy requirements.
The most common hybrid cloud example is combining a public and private cloud environment, like an on-premises data center, and a public cloud computing environment, like Google Cloud.
Multi-cloud
Multiple public clouds are referred to as "multi-cloud." A business that employs numerous public clouds from various cloud providers includes a multi-cloud setup. In a multi-cloud arrangement, a business uses multiple vendors rather than relying just on one for cloud hosting, storage, and the entire application stack.
A company might, for instance, utilize Microsoft Azure for disaster recovery, AWS for data storage, and Google Cloud Platform for development and testing.
Cloud computing Service providers
A cloud service provider is a third-party company offering a cloud-based platform, infrastructure, application, or storage services. Much like a homeowner would pay for a utility such as electricity or gas, companies typically have to pay only for the amount of cloud services they use, as business demands require.
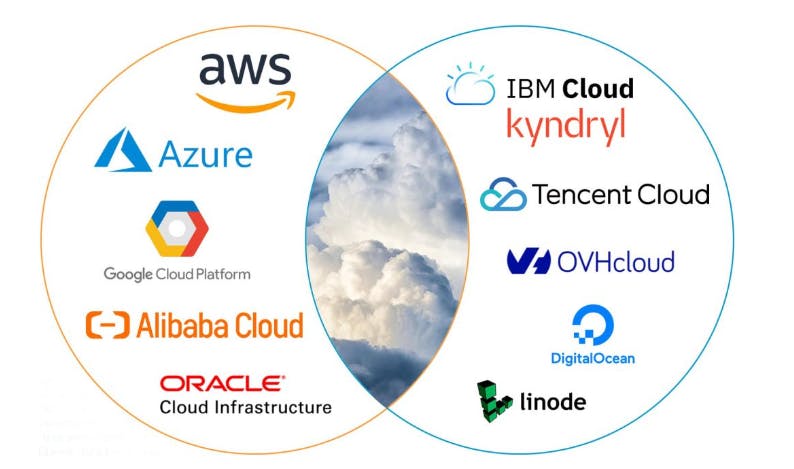
Types of cloud service providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Alibaba Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- IBM Cloud (Kyndryl)
- Tencent Cloud
- OVHcloud
- DigitalOcean
- Linode (Akamai)
Which Cloud Service Provider Has the Largest Market Share?
The three cloud service providers with the greatest market shares—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)—acquire approximately 65% of the money spent on cloud infrastructure services. The top 10 cloud service providers are included in the table below, with a focus on AWS, which holds a 34% market share, Microsoft Azure, which holds a 22% market share, and Google Cloud, which holds a 9.5% market share.
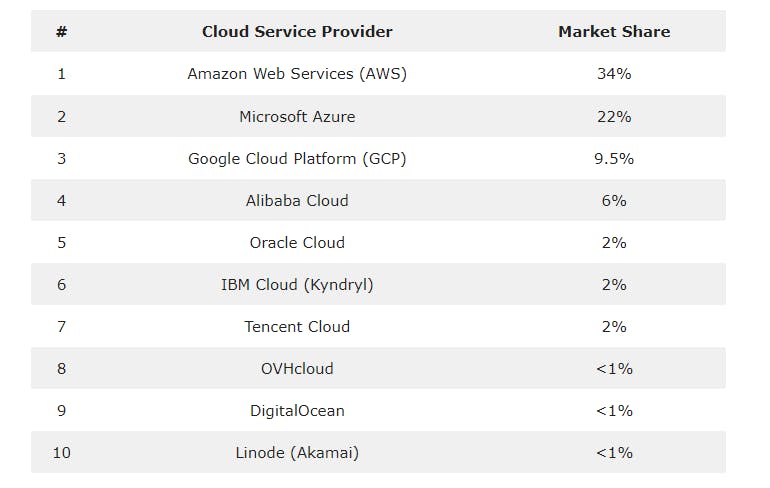
AWS has consistently increased its market share from its prior base of 5% over the past five years, while Microsoft Azure has aggressively increased its market share from its historical low of 10%. Google Cloud has also been steadily growing its market share. Over this time period, there were market share gainers as well as corresponding market share losers, including IBM Cloud (Kyndryl) and a number of tiny cloud service providers.
What are the pros of cloud computing
It just makes financial sense, which is why cloud computing has grown so popular among businesses all over the world. Let's take a closer look at what this technology can accomplish for you as you may not be aware of all the advantages of cloud computing. The top ten reasons to shift your company to the cloud are as follows.
1. LOWER THE COSTS OF INFRASTRUCTURE
Companies spend a lot of money on internal data storage. Both the upfront cost of buying each new server and the cost of installing them are involved. Either you have to pay the vendor to handle the installation, or your IT team has to take time out of their busy schedules to execute it. The device must then be periodically backed up and properly maintained.
Even when you invest in the best tools, human error is always a possibility. If your staff installs and maintains the system, and they make a mistake, there is no one to turn to for help. With cloud computing, you no longer have to worry about maintaining internal systems because your service provider will help you. You save money since the cost of the infrastructure is covered by your plan and shared by all of the clients of the service provider.
Businesses that use cloud computing services annually save more than 35% on operating expenses, according to a survey on the global cloud services market.
2. THE EFFECT ON PERSONNEL
The cost of keeping an internal IT team large enough to operate local servers can rise quickly. The time and money spent on hiring and training are all done in the hopes of creating a committed and highly successful worker, but that isn't always the case. Some workers will perform below expectations, while others might choose to leave the company. IT industry turnover costs businesses 150 percent of an employee's compensation.
The benefits that come with having an in-house staff come at an additional expense, which cloud services can help offset. Your in-house team can be refocused, or you can avoid the expense of future team expansion, while your service provider takes care of maintenance and backups.
3. COMBINE YOUR DATA.
Data is dispersed among bi-coastal data centers using cloud storage. Data can be linked and updated fast thanks to synchronization technology, but syncing is not required when data is stored in the cloud. You always know exactly where each piece of information is when it is all stored on the cloud.
4. PREVENT CATASTROPHES
Losing data may be disastrous for any size of business. Globally, data breaches cost an average of $3.86 million, and they cost American businesses an average of $7.91 million. Operating a data center on-site is far less secure than using cloud-based storage. When compared to companies that employ cloud storage, those who store their data on-site experience a 51 percent higher rate of security problems.
Cloud storage services offer enterprise-level security that is significantly superior to what most small and medium-sized businesses (SMB) can afford on-site. There isn't a single point of failure, which is one benefit of using the cloud to store data. Your data is replicated across multiple servers so that even if one of them crashes, your organization's data is still safe and secure.
Many businesses have taken precautions to prevent this fatal gap in storage security, which is what caused the notorious Equifax and Verizon data breaches. One option for businesses to get rid of this risk is through cloud storage.
5. IMPROVE UPTIME
Unplanned downtime has a significant financial impact that cannot be overstated. An average business loses $5,600 for every minute of unanticipated downtime brought on by a data center failure. $300,000 was made in under one hour. The productivity lost during that period is money you won't be able to recover, even though employees may like the extra time spent in the break room. If unplanned downtime has a negative impact on clients, it can also seriously harm a company's brand.
System failure and human mistakes are the main sources of unplanned downtime, and both may be prevented. One poll found that 61% of SMBs who switched to the cloud saw fewer occurrences of outages and a reduction in the duration of the downtime that did happen.
6. To Strengthen Cooperation
Because of the capacity to collaborate digitally, businesses are thriving today. Because of how advantageous remote work is for businesses, 56 percent of startups outsource some of their labor. Employees enjoy it as well; 57 percent of those employed in the computer and IT sector work in some capacity from home. Additionally, it is now more common than ever for businesses to have staff working all over the world, making collaboration skills essential.
Using cloud computing, numerous employees may see and edit files and documents in real-time, making it much easier for team members to work together on projects. Accessing documents in the cloud makes it easier to ensure that everyone is using the most recent version of a document and to prevent the spread of outdated copies among local sources.
7. STAY ADAPTABLE
How might cloud computing help your business grow? One of the problems of growing is staying scalable. You can use this solution to only pay for the storage space your company actually uses. You have two choices if you discover that your company is expanding quickly enough to necessitate the need for more storage.
You have the option of adding more equipment and hiring the staff you'll need to keep it running. With the necessary planning and training time, you can anticipate having your enhanced capacity operational in a few weeks to a month or more.
Or, you might give your cloud storage service provider a call and ask them to quickly raise your capacity. Increasing cloud also has predictable costs, which removes the risk involved with making investments in new storage equipment. Your firm will become more nimble and competitive regardless of its industry if you have a greater ability to raise or decrease your storage capacity as necessary.
8. AMPLIFY AUTOMATION
Regular backups are an important part of sustaining internal data storage. The IT department must set aside time to plan backups around daily activities. To free up your staff to focus on the tasks that advance your company, cloud computing services go a long way toward automating these routine backups.
9. CONSERVE SPACE
In-house system expansion frequently necessitates careful planning to secure the appropriate amount of space due to the substantial square footage required by servers and all of their accompanying equipment. Larger firms may have more room to expand, but smaller businesses frequently struggle to make the most of every available square inch. By removing the need to prepare for future equipment expansion, cloud computing can free up space in your office for additional amenities or workstations. You do not need to worry about installing specialized HVAC systems, high-voltage lines, backup generators, or even dedicated breakers.
10. IMPROVE COMPLIANCE
The countless rules that apply to various forms of data are difficult to comprehend, time-consuming to implement, and labor-intensive to maintain. Why not delegate the labor-intensive aspects of compliance to a cloud storage service provider? You need not be concerned about breaking any laws because a good provider complies fully with all relevant rules.
What are the cons of cloud computing
What are the drawbacks of online storage? It is difficult to ignore the benefits of cloud storage. The top five issues that businesses encounter with moving to the cloud are as follows.
1. UNDERSTANDING THE COSTS
Although moving to the cloud can help cut expenses in some areas, it is crucial to make sure that the move is justified. A proper plan must be implemented, and all organizational structures must be examined. The secret is to analyze the systems and divide them into two groups. Systems that ought to be migrated to the cloud and those that ought to stay on-premises fall under these two groups. You can then decide on a budget for the project once this has been determined.
2. FROM CLOUD TO ON-PREMISES TRANSITION
Your company may typically transition from on-premises servers to cloud data centers without much difficulty. Even while this is the case, switching to a different cloud provider or going back to an on-site server is not as simple. The costs associated with this procedure might actually add up, and the terms frequently favor the cloud provider. Make sure to inquire about and comprehend the procedure for relocating workloads out of the cloud supplier's data center before selecting whether or not to sign a contract with them. Covering the deadlines, penalties, and procedure is essential.
3. SMALL CONTROL
Businesses may be concerned that they won't have enough control over the service because the service provider owns and manages the cloud infrastructure. The end-user license agreement (EULA) of the provider may be able to assist you in this situation. It describes the restrictions the supplier may impose on how you utilize the deployment. Even if they don't let you make any changes to the architecture, all reputable cloud computing companies let your business exercise control over its applications and data.
Make sure you comprehend every term of the service level agreement (SLA) that the supplier gives you. This will enable you to confirm what is permitted and prohibited from using the service.
It's critical to know how close a cloud supplier's data center is to your workplace if your contract calls for you to store your own hardware there (such as at CoLo). Get the complete list of information regarding how to access the equipment in case that it needs maintenance.
4. PROVIDER LOCK-IN
Vendor mismatches may represent one of the drawbacks of cloud computing. When transferring services to a different vendor with a different platform, organizations may experience difficulties. It's possible for data to be exposed to unnecessary vulnerabilities if this process isn't managed properly. The ability to safely migrate your data between suppliers is a skill that a reputable cloud services provider possesses.
5. RESTORES AND SLOWER BACKUPS
Due to the high communication latency involved in sending data to the cloud, backups may end up taking longer than they would with an internal system. This typically isn't a problem, not even for larger, full backups. The initial, larger backups take longer, but they can operate in the background without interfering with networks.
It can take longer if you have to restore the entire server. However, specific files and folders probably won't be affected. If you choose the correct provider, speed differences are barely noticeable.
6. WEBSITE RELIABILITY
The fact that cloud computing is totally dependent on the internet is a slight disadvantage. For the length of the outage, you won't be able to access data saved in the cloud if your internet connection drops. An internet outage won't jeopardize or erase your cloud-stored data, though. Cloud computing is essentially the same as any other web-based technology because practically every operation of your business requires the internet.
7. WEBSITE USE
Large backups to the cloud have the potential to cause congestion and degrade your internet performance if they are being done during business hours when internet usage is high. Small businesses that lack the funds to invest in the fastest internet bandwidth and speeds are the ones most impacted by this problem. However, a competent service provider would collaborate with you to find a solution through automation or scheduling.
Characteristics of cloud computing
Resources Pooling
On-Demand Self-Service
Easy Maintenance
Scalability And Rapid Elasticity
Economical
Measured And Reporting Service
Security
Automation
Resiliency And Availability
Large Network Access
Work From Any Location
Multi-Tenancy
Flexibility
Service Excellence
Comfortable Payment Structure
1. Resources Pooling
One of the fundamental elements of cloud computing is resource pooling. By using resource pooling, a cloud service provider can distribute resources across a number of clients, offering everyone a unique set of services based on their needs. It is a multi-client approach that can be used for services that provide bandwidth as well as data storage and processing. The method of assigning resources in real-time does not interfere with the client's experience.
2. On-Demand Self-Service
It is an important and fundamental aspect of cloud computing. It enables the client to continuously keep tabs on the availability, capabilities, and allotted network storage of the server. This is a core feature of cloud computing, and a client can also regulate the computer power to suit his requirements.
3. Easy Maintenance
One of the nicest cloud qualities is this one. The servers are easily maintained, and there is occasionally little to no downtime. Resources that are driven by cloud computing frequently receive updates to maximize their potential and capabilities. The updates work faster than the older versions and are more compatible with the devices.
4. Rapid Elasticity and Scalability
Rapid scalability is a significant feature and advantage of cloud computing. Due to this cloud feature, workloads that call for a large number of servers but are only needed temporarily can be performed cost-effectively. Such workloads are common among clients and may be managed extremely economically because to cloud computing's quick scaling.
5. Economical
This attribute of the cloud aids in lowering enterprises' IT spending. In cloud computing, the user must reimburse the administration for the consumed space. There is no hidden fee or extra cost that must be paid. Since the administration is frugal, some space is typically given up for free.
6. Measured And Reporting Service
One of the numerous features of the cloud that makes it the greatest option for enterprises is reporting services. Both cloud service providers and their clients can benefit from measuring and reporting services. It makes it possible for the client and the service provider to keep track of and report on which services have been used and for what reasons. This promotes resource efficiency and aids in billing oversight.
7. Security
One of the best aspects of cloud computing is data security. To avoid any kind of data loss, cloud services create a copy of the data that is saved. In the unlikely event that one server loses the data, the backup copy is recovered from the other server. This functionality is helpful when multiple people are simultaneously working on the same file and the file unexpectedly becomes corrupted.
8. Automation
Cloud computing must have automation as a key component. Automation in cloud computing refers to the capacity of a cloud service to be installed, configured, and maintained automatically. In layman's words, it is the practice of maximizing technology while minimizing physical labor. Automation is not, however, as simple to achieve in the cloud ecosystem. Virtual machines, servers, and a lot of storage must be installed and deployed. These resources require ongoing maintenance even after the successful deployment.
9. Resiliency And Availability
In cloud computing, resilience refers to a service's capacity to resume operations as soon as a disruption occurs. How quickly servers, databases, and the network system of a cloud can restart and recover from any damage or harm is a measure of the cloud's resilience. Another important aspect of cloud computing is availability. There are no geographical restrictions or limitations while using cloud resources because cloud services can be accessed remotely.
10. Access to a large network
The cloud's ubiquity makes up a significant portion of its properties. With simply a device and an internet connection, the client can view the cloud data from any location and upload data to the cloud. These capabilities are available throughout the company and are accessed with the aid of the internet. By tracking and ensuring specific metrics that indicate how users access cloud services and data, such as latency, access time, data throughput, etc., cloud providers minimize the need for a huge network connection.
10. Work From Any Location
One of the main aspects of cloud computing is remote working. Thanks to it, users can work remotely or from any point on the earth. Users will be allowed to use mobile devices like laptops and smartphones to access business data. Additionally, it makes sure that everyone can connect fast. Employees that commute or live elsewhere can still communicate and carry out their duties.
12. Multi-Tenancy
The Multi-Tenancy of cloud computing is one of its best features. With the use of the multi-tenancy software architecture, many user groups can be served by a single instance of a program. It means that several clients of the cloud provider are utilizing the same computing resources. Each Cloud customer's data is kept fully separate and secure even though they use the same computing resources.
13. Flexibility
As the competition grows, the business must scale. Users who already use the conventional hosting method will need to change service providers. When users host their data in the cloud, they have more freedom. Scaling can be done at any moment and does not require a server restart. For users, a range of payment options are also accessible. This suggests that companies won't have to spend excessively on resources they don't require.
14. Service Excellence
Users always obtain the best level of service thanks to cloud computing. Benefits stated in Service Level Agreements must include extensive resources, constant availability, and bandwidth. Any compromise on these services will lead to a drop in popularity and a loss of customers.
15. Comfortable Payment Structure
The payment system is important since it helps with cost-cutting. Cloud computing options have a variety of pricing due to the added capability. The payment option is straightforward for users to use, and it helps them save time when processing payments frequently.
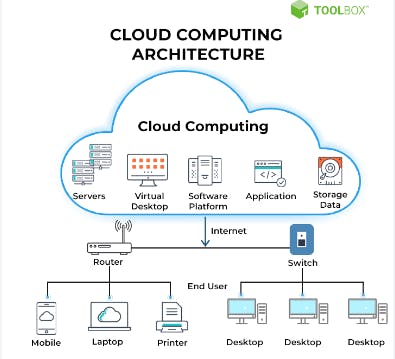
Types of cloud services
Infrastructure, platforms, or software that are hosted by external providers and made accessible to users online are referred to as cloud services. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are the three primary categories of as-a-Service solutions. Each one supports the transfer of user data from front-end clients to the cloud service provider's servers and back, but they differ in the features they offer.
- IaaS(Infrastructure as a service)
IaaS stands for a cloud service provider that uses an internet connection to handle your infrastructure, including the real servers, network, virtualization, and data storage. The user essentially rents the infrastructure and has access via an API or dashboard.
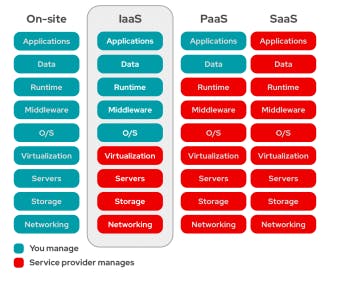
While the provider handles any hardware, networking, hard drives, data storage, and servers, and is in charge of handling outages, repairs, and hardware issues, the user is in charge of things like the operating system, apps, and middleware. This is how most cloud storage companies deploy their systems.
- PaaS(platform as a service)
PaaS refers to an external cloud service provider providing and managing the hardware and an application-software platform, but the user is in charge of the apps that run on top of the platform and the data such apps rely on.
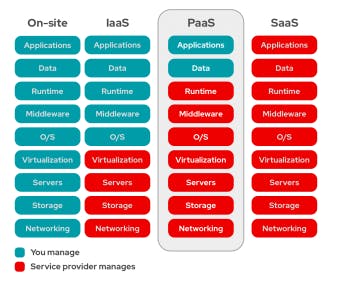
PaaS provides users with a shared cloud platform for application development and management (a crucial DevOps component) without their having to construct and maintain the infrastructure typically involved with the process. It is primarily for developers and programmers.
- SaaS(Software as a service)
SaaS is a service that gives consumers access to a piece of software that the cloud service provider administers. SaaS apps are often web or mobile applications that consumers can access using a web browser.
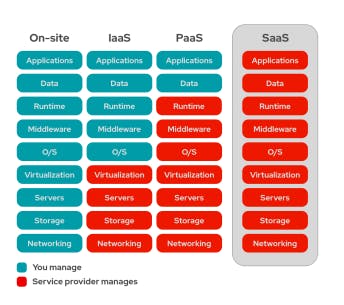
Users connect to the cloud applications via a dashboard or API, and updates, bug patches, and other routine software maintenance are handled for them. SaaS also removes the requirement for a program to be locally installed on each user's computer, opening up more options for group or team access to the software.
below are the types of service providers that provide each of these services
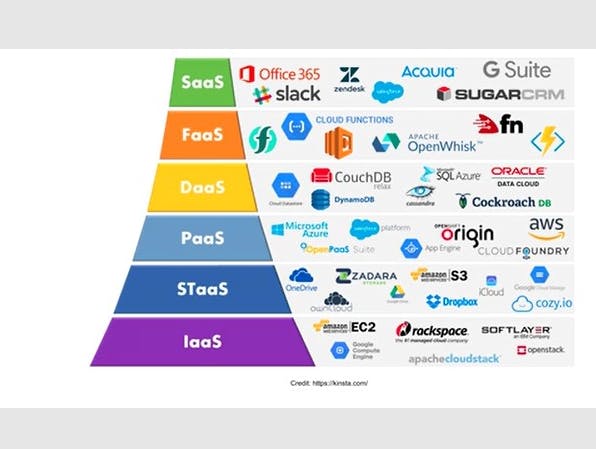
Uses of cloud computing
There are numerous applications for cloud computing that can give businesses a competitive edge. Consumers can use the Internet to pay-as-you-go access cloud services thanks to the cloud computing concept and related technologies.
Cloud computing is gaining popularity day by day even though it is a relatively new paradigm that just recently gained widespread acceptance.
The numerous applications of cloud computing have demonstrated their effectiveness in offering a range of solutions to diverse problems for government agencies, NGOs, non-profit organizations, and small start-ups.
Having said that, has your company embraced cloud computing? If you haven't, it's probably because you don't comprehend its applications and the advantages it can provide for your company.
Here are a few typical applications for cloud computing that should get you thinking about how this technology may help your company.
1. Storage of files
Your data can be stored and accessed in a variety of ways. The hard drive in your laptop, the external hard drive you use for data backup and transfer, network file sharing, USB drives, and more are all examples of storage devices.
What distinguishes cloud storage from the other available storage options?
Well, the biggest benefit of cloud storage is the simplicity with which files may be viewed and updated. Your files are accessible from any device, anywhere, with just an internet connection.
Cloud storage comes in a variety of forms, including block, file, and object storage. Each of them is appropriate for a distinct use case, including block-based volumes, backup and archiving systems, and shared filesystems.
You can gain safe access and scalability to add or decrease storage based on your demands and budget with cloud computing storage services like Amazon S3, DropBox, or OneDrive. Because of this, this kind of storage is not only very economical but also quite safe.
2. Analytics for Big Data
If your company doesn't gather big data now, it will be at a serious disadvantage. Data on your clients, market trends, sales performance, and more may be included.
Big data is necessary for businesses of all sizes for a variety of reasons. Some people gather it to identify fresh chances for commercial expansion, while others do it to find answers to challenging issues.
But gathering and interpreting massive data is challenging. It necessitates the employment of significant computing resources, which are expensive.
Budgets for other crucial services like marketing may need to be cut if you decide to buy the resources required for cloud computing. When you use cloud computing, you can avoid doing this.
The fact that cloud computing has a pay-as-you-go pricing model is its main advantage. This means that you won't have to pay for any time that is not used, which will result in big financial savings for your company. You only use and pay for resources when you actually need them.
Without a question, big data analytics are made easy, practical, and affordable by cloud computing. For additional information, check out the many analytics capabilities Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers for a range of use cases.
3. Data archiving and backup
Cybercrime is a common occurrence in the world we live in today. There are always going to be significant data breaches, which may sometimes be catastrophic for a lot of firms.
For a very long time, traditional data backup techniques have been successful in protecting data. However, they are susceptible to infections, and because they are movable, they can disappear and represent a risk to contemporary businesses.
An answer to these problems is cloud-based backup and archiving. It offers the highest level of data protection and is simple to apply. You can backup or archive your sensitive files using this method to cloud-based storage platforms. In the event that your live data is somehow compromised, you can rest certain that your data is still secure thanks to this.
You may schedule backups with some cloud computing services to suit your particular requirements. You can also encrypt your cloud backups to deter hackers and snoopers from accessing them.
With cloud storage, you only pay for the space and data that you really use. You can acquire as much room as you need.
4. Recovery from disaster
Do you realize the price of failing to implement a business continuity plan? According to research, more than 75% of companies that suffer a crisis but do not have a disaster recovery plan in place collapse three years after the incident.
Building a disaster recovery site and performing business continuity plan testing have historically been very expensive and time-consuming tasks.
But it's no longer necessary for it to be that way!
You can create a disaster recovery system using cloud computing. In this technique, you build a copy of your production site and duplicate data and configuration settings on it continuously.
Your apps and data services may be quickly and easily launched in the cloud in the case of a disaster at your production location, allowing you to quickly resume operations.
CloudEndure by AWS is an illustration of an automated and coordinated disaster recovery system. To find out how to automate your disaster recovery, read this blog post.
5. Software development and testing
If you've ever created internal software or an application, you know how time-consuming, costly, and expensive the process is. Installation and configuration of complex technology and software are required, as well as ongoing staff member training.
Simply said, this implies that even a straightforward job can take months to complete, which could put you at a disadvantage in the fiercely competitive market of today.
Numerous solutions for continuous integration and continuous delivery are available from cloud computing providers, which speed up, simplify, and lower the cost of development and testing.
Check out the FREE AWS cheat sheets from Digital Cloud Training if you're interested in learning everything there is to know about the Developer Tools provided by AWS.
By reducing the time it takes for software to be delivered, these cloud development tools can give you an advantage over your rivals.
6. Platform as a service and infrastructure as a service (PaaS)
Significant investments must be made in acquiring and managing IT infrastructure in order to run the physical servers and virtualization infrastructure that will host your virtual machines.
Businesses are using cloud computing, whose pay-per-use pricing model delivers the ideal balance of quality and affordability, to save expenditures on this. You can say goodbye to your VMware licensing expenses as well as all of the hardware that you use to host your virtual servers using Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
This is due to the fact that IaaS eliminates the need to handle any of the hosting software or hardware by allowing you to simply deploy virtual machines, also known as "instances," in the cloud.
What happens, though, if you don't even wish to control the instances' operating systems? Platform as a Service (PaaS) can help in this situation. When adopting the PaaS computing paradigm, all that is required for you to launch and operate your application in the cloud is for you to upload your code to the cloud provider.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a prime illustration of a PaaS service. Your Amazon EC2 instances, Auto Scaling groups, Elastic Load Balancers, and even Amazon RDS databases can all be built out using this service by simply uploading your code. Elastic Beanstalk will then take care of the rest.
7. Communication
People may use cloud-based communication tools like calendars and emails thanks to cloud computing. Additionally, all messaging and calling apps, including Skype and WhatsApp, are built on cloud infrastructure.
The cloud service, not just your device, stores the data and messages you send and receive. This enables you to access them via the internet from any device and location on the planet.
8. Social media networking
Social networking is arguably one of the most underappreciated uses of cloud computing. The Software as a Service (SaaS) cloud computing concept is an example of which are websites like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
Platforms for social media were created to make it easier to connect with individuals you don't know or to find those you do. They also provide you with a variety of methods for exchanging data and information, including tweets, pictures, instant chats, and posts.
Social networking is one of the most popular use cases for consumer-driven cloud service utilization, along with cloud storage.
9. Business procedures
You have already incorporated cloud computing into your management approach if you use company management software like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Using software as a service (SaaS), which mainly relies on cloud computing paradigms, these enterprise-level apps are deployed. They guarantee straightforward resource management, security, and upkeep for your company. Additionally, they give service providers and their clients with the highest level of efficiency.
Conclusion
Without a doubt, the market for cloud computing is expanding, and its services can be used for a variety of beneficial purposes. The cloud is quickly becoming the preferred platform for software testing and development, communication, storage, and deployment in new businesses.
With the information provided above regarding cloud computing, there is no excuse for you not to use it in your company right away to get a competitive edge.